Dr. Shameem Shariff
MONTHLY QUIZ
(Page CLOSED - JAN 2026)
Dr. Shameem Shariff, MD, PhD
Formerly, Professor and Head,
Dept. of Pathology, MVJ Medical College and Research Hospital &
St. John's Medical College,
Bengaluru, India
www.shameempathology.com
DECEMBER 2025
HISTOPATHOLOGY
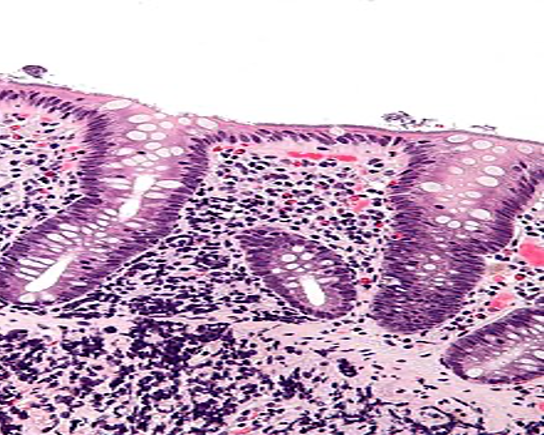
Fig shows an endoscopic biopsy from a 54 year old individual. Identify the anatomical part of the intestine. What is the pathology. With what clinical symptoms do these patients present? (see surface epithelium)
Ans to previous : (November 2025)
Parathyroid adenoma. Parathyroid hormone was elevated.
CYTOPATHOLOGY
Figs 1 and 2 from a mass in the right hypochondriac region.
Make your diagnosis.
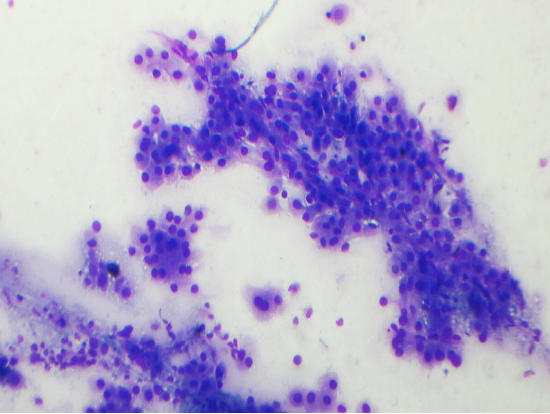
Fig 1 : Giemsa x 100
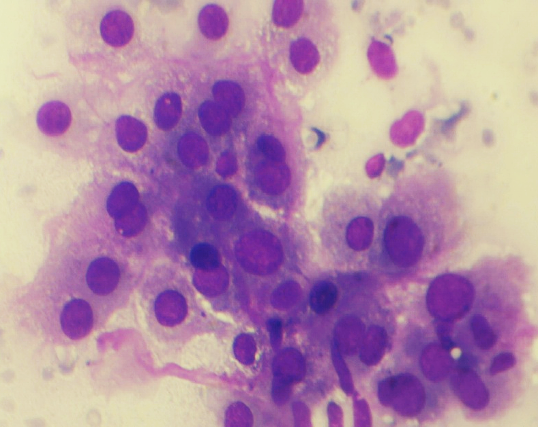
Fig 2 : Giemsa x 400
Ans to previous (November 2025):
Highly suggestive of papillary adeno-carcinoma Endometrium - Shows adequate cellularity with papillae of carcinoma cells showing hyperchromatic and pleomorphic nuclei, highly suggestive of papillary adenocarcinoma of the endometrium.
TECHINQUES
What is the principle of functioning of a rotary microtome? Is it commonly used in the lab?
Ans to previous (November 2025):
Ans to previous :
Name 2 applications of karyotyping.
A. Genetic disorders: it helps in detecting genetic diseases and arriving at a clinical diagnosis in patients with congenital abnormalities, delayed milestones and mental retardation.
B. Repeated fetal loss: occur due to chromosomal aberrations and result in spontaneous abortions in the first trimester of pregnancy. Karyotyping helps in the detection of these.
MCQ
Which of the following statement/s is TRUE regarding cytologic features of malignancy?
(a) Nuclei may become larger and more hyperchromatic
(b) Nuclear borders become irregular in thickness.
(c) Nuclei may become larger and hypochromatic
(d) Cytoplasm may become more eosinophilic.
Ans to previous (November 2025)
A. Germ Cell Tumours
NOVEMBER 2025
HISTOPATHOLOGY
Ultrasonically guided fine needle aspiration cytology of a mass in front of the neck of a 40 year old female. Patient complained of severe back ache and had osteoporosis. Fig 1 and Fig 2 : are shown. Make your diagnosis.
Fig 1
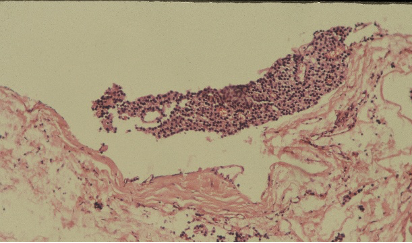
Fig 2

Ans to previous : (August 2025)
Tumour embolus in a lymphatic channel.
CYTOPATHOLOGY
Endometrial Aspirate in a 35 year old female (using Intracath cannula ) and complaining of increased bleeding during mensus. Make your diagnosis.

Ans to previous (August 2025):
The diagnosis at aspiration is ‘fibroadenoma’. The history of slipping of edge at palpation together with ‘antler pattern’ and the shower of bare nuclei in the background clinch the diagnosis.
The unusual feature seen in this aspirate is presence of giant cells. Other unusual features seen on aspiration of a fibroadenoma, at times, could be enlargement or enlarged epithelial cell nuclei, hyperplasia, apocrine metaplasia and abundant fibromyxoid stroma.
TECHINQUES
Name 2 applications of karyotyping.
Ans to previous (August 2025):
The Haematoxylins are classified based on the mordant used in the haematoxylin : whether Alum (ammonium or potash alum) or Iron :
A. Alum haematoxylin eg. Delafield’s, Ehrlich’s, Mayer’s, Harris’ and Coles.
B. Iron haematoxylins (uses ferric Ammonium sulphate and Ferric chloride) eg. Weigert’s Iron Haematoxylin.
The main advantage of using Weigert’s iron haematoxylin is where acidic staining solutions are to be applied to the sections eg. in Van Gieson stain. It resists decolorization better than alum hematoxylins ie aluminium based formulations.
MCQ
A 4 year female is detected as having a solid ovarial tumour mass on the left side. Which ?
A. Germ cell tumours
B. Sex cord stromal tumours
C. Surface Epithelial tumours
D. Metastasis
Ans to previous (August 2025)
A. Morphology of the specimen is preserved consistently as in conventional, manual tissue processing.
AUGUST 2025
HISTOPATHOLOGY
What is the lesion seen in this section ?
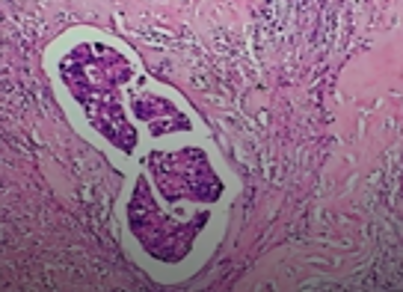
Ans to previous : (July 2025)
Lactating adenoma breast. The breast acini in all lobules are hyperplastic with cells showing secretary change.
CYTOPATHOLOGY
Aspirate from a mass in the right breast of a 30 year old female, slips on palpation. Make you diagnosis. Give 2 points in favour of it. What unusual findings do you see in the lesion?
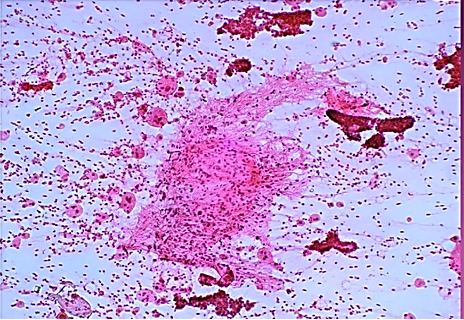
Ans to previous (July 2025):
The cluster of cells in the centre of the field appear to be endocervical in origin. (Note the cytoplasmic tails on the right margin of the cluster).
They do not show any abnormality.
TECHINQUES
How are Haematoxylins classified? Give examples
What is the advantage of using Weigert’s haematoxylin?
Ans to previous (July 2025):
Post – chromation: Is secondary fixation to demonstrate certain morphological details.
It is the treatment of tissues with 2.5 % or 3% potassium dichromate after normal fixation.
Method : It may be carried out either before processing when tissues are left for 6-8 days in dichromate solutions or after processing when sections before staining are immersed in the dichromate solution for 12- 24 hours followed in each case by washing well in running water.
Advantages : This technique is employed to mordant tissues for staining, particularly cytoplasmic organelles such as mitochondria and chromaffin tissue. It gives improved preservation and staining of these elements. Phospho-lipids are also more resistant to extraction with post chromation, eg. as in Weigert’s method for myelin.
MCQ
What in you opinion is the main advantage of automation in a laboratory for tissue processing ?
A. Morphology of the specimen is preserved consistently as in conventional, manual tissue processing
B. Vacuum facility
C. Capacity in a large number, up to 360 cassettes
D. Fixation to paraffin infiltration
has a unique linear design
Ans to previous (July 2025)
Ans : b, Resolution
JULY 2025
Quote : The purpose of education is to replace an empty mind with an open one - Malcolm Forbes
HISTOPATHOLOGY
Section from a well circumscribed swelling in the breast of a pregnant lady. What change are the acini showing? What do you think is the lesion?
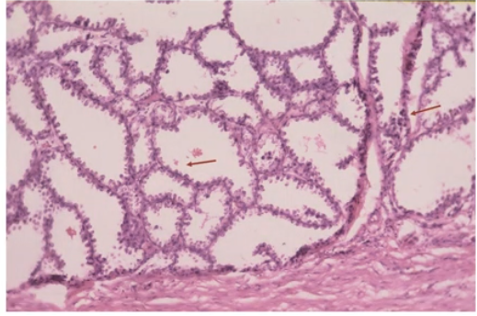
Ans to previous : (June 2025)
Maltoma – small intestine- monocytoid B cells many showing plasmacytoid differentiation.
Patient had t(14;18)(q32;q21)
CYTOPATHOLOGY
Vaginal smear in a 54 year old lady. Identify the cluster of cells in the centre of the field. Are they normal or abnormal?
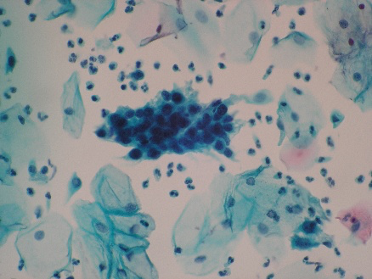
Ans to previous (June 2025):
The squamous cells show clearing of the perinuclear space and irregular nuclear contours , typical of LSIL. Changes are in keeping with koilocytotic atypia.
TECHINQUES
What do you understand by post-chromation?
How is it done?
What are the advantages?
Ans to previous (June 2025):
3. Technique –
Endometrial specimen collection
Smears from the posterior fornix show exfoliated endometrial cells.
Endocervical smears show endometrial cells
Endometrial brush cytology
Intrauterine aspirations .
Intrauterine aspirations yield the best smears.
Endocervical smears
Ayre’s spatula
After taking the smear, the spatula is rotated evenly on a glass slide in multiple clockwise swirls andd fixed immediately.
Most gynaecologist smear one slide with endocervical material and a second slide with ectocervical material.
Wooden spatulas
Multispatula
The main advantage of multispatula is to increase the endocervical cell content. At the cervical end the body has two wing like protuberances which surround the central portion. The sliding into the endocervical canal is controlled by a button and allows an endocervical penetration of 8 mm when fully extended.
Cytobrush
The Cervex Brush
Combined spatula and cytobrush technique: is a very effective sampling combination for both the endocervix and the ectocervix
MCQ
In the normal course of events a thrombus in a vein undergoes –
a. Organisation
b. Resolution
c. Embolism
d. It propagates
Ans to previous (June 2025)
Ans – 1. High grade carcinomas are often +ve for p53
JUNE 2025
Quote : Education’s purpose is to replace an empty mind with an open one - Malcolm Forbes.
HISTOPATHOLOGY
Section H and E x400. Mass in the wall of the small intestine in a 72 year old male patient who presented with frequent diarrhoea. Make you diagnosis.
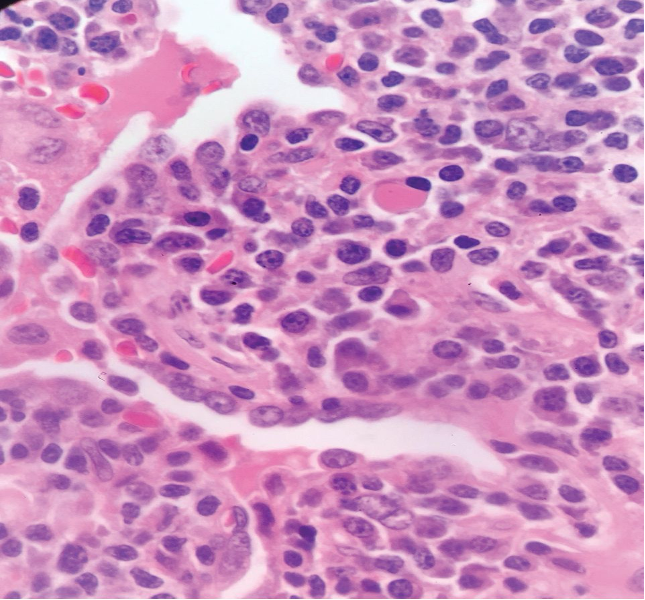
Ans to previous : (May 2025)
Sertoli -Leydig Cell tumour moderately differentiated . Note well formed Sertoli cell tubules. Occasional Leydig cell in the stroma.
DICER 1 mutation is one of the mutations (germline or Somatic ) seen in these type of tumours. Patients with these germ line mutations are younger, and can have other tumours. Tumors and disorders associated with DICER1 syndrome include pleuropulmonary blastoma, cystic nephroma, multinodular goiter and botryoid embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma.
(Germline DICER 1 mutation is a gene encoding the RNase III enzyme in the microRNA maturation pathway.)
CYTOPATHOLOGY
Cervical smear from a 56 year old female. Describe the changes and give your diagnosis.
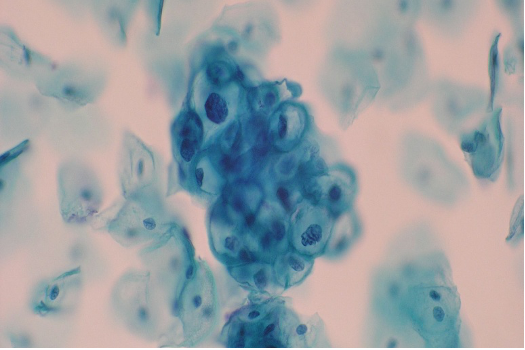
Ans to previous (May 2025):
The diagnosis on this structure is “microfilaria”.
This organism can be aspirated and a diagnosis made on breast, thyroid, lymphnode , scrotal and other soft tissue superficial swellings in areas like the tropics and subtropical regions where filariasis is endemic. It can be the sole cause of swelling or incidential finding associated with other pathology.
TECHINQUES
Name all the devices which enable endometrial/endocervical sampling for smears.
Which in your opinion gives the best yield?
Ans to previous (May 2025):
In order to negate presence of a carcinoma 3 consecutive morning samples (which yield maximum cells) are examined before a negative report is given.
MCQ
The following characteristics are intrinsic to papillary serous carcinoma of the endometrium :
1. High grade carcinomas are often +ve for p53
2. It is ER +ve
3. It occurs in a younger age group as compared to the endometroid endometrial carcinoma
4. It is often associated with atypical endometrial hyperplasia
Ans to previous (May 2025)
d. All of the above
MAY 2025
Quote : Education is the best weapon which can change the world - Nelson Mandela
HISTOPATHOLOGY
A 30 years old female presented with hirsutism, clitoromegaly and atrophy of her breats. On imaging of the abdomen a right ovarian mass was seen, measuring 15 cms in size . Section from the mass is shown.
Make your diagnosis. What is the importance of DICER 1 gene?
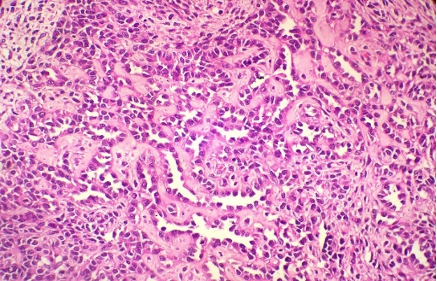
Fig 1
Ans to previous : (March 2025)
Adrenal cortical carcinoma.
Differentials :
Renal cell carcinoma
Adrenal cortical neoplasm
Pheochromocytoma
CYTOPATHOLOGY
FNAC done on thyroid glad in a female patient ; incidentally aspirated the structure seen above . Is this an artefact ? or not ? if not make your diagnosis.
Where else is this picked up on aspiration?
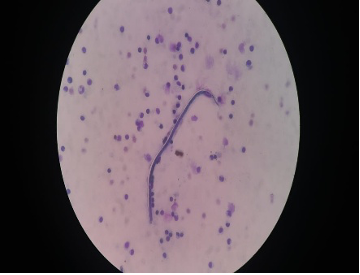
Ans to previous (March 2025):
Excision of the specimen showed a cystic neoplasm (Figs A and B)
Diagnosis: Parathyroid adenoma .
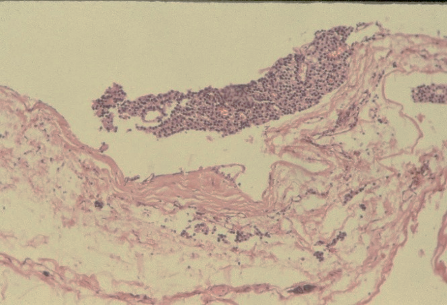
Fig A
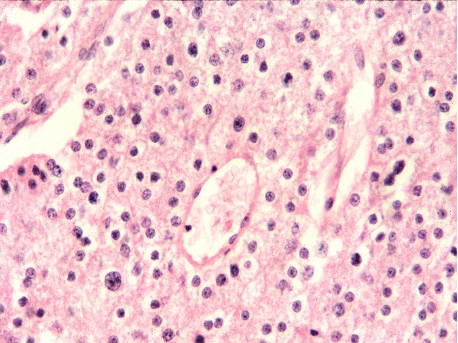
Fig B
TECHINQUES
How many urine samples, and collected when, should be examined before a negative for carcinoma result is given, on urine microscopic examination ?
Ans to previous (March 2025):
Recommend genetic testing is clinically advocated in anyone diagnosed with triple-negative breast cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, colorectal cancer before age 50, metastatic prostate cancer, or male breast cancer.
Some of the familial Cancers show losses of the following genes :
Gene Consequence of gene loss
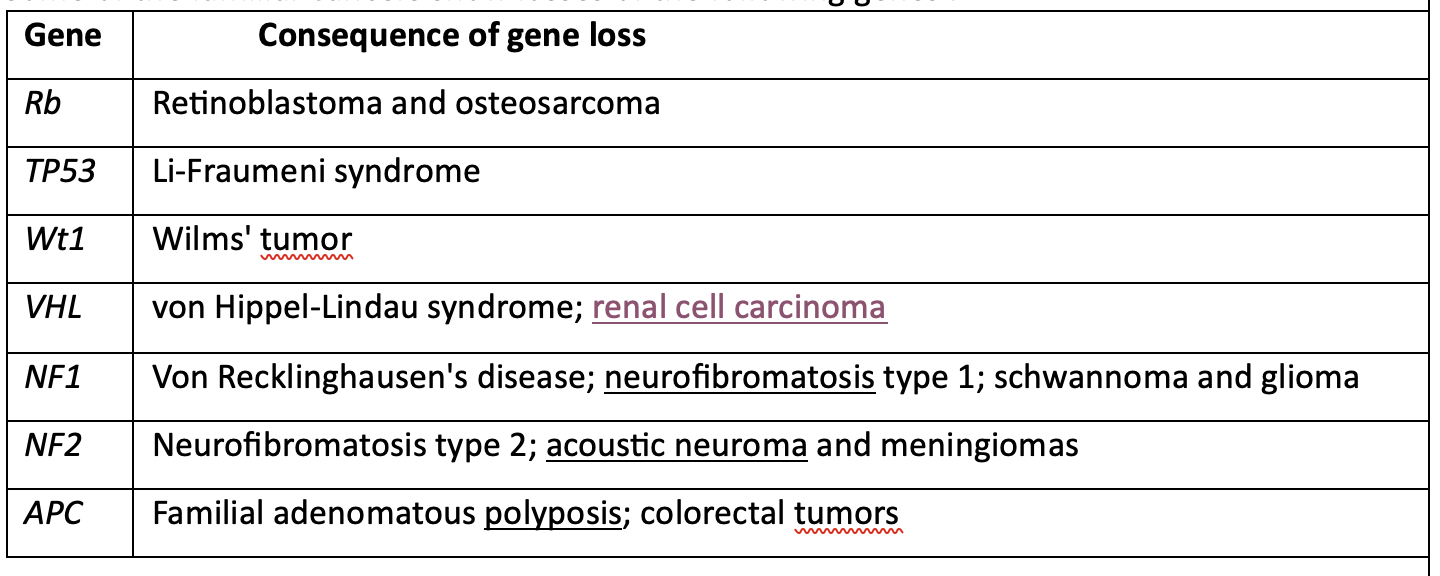
MCQ
Osteomalacia is a term used for –
a. Occurrence of rickets in the adults
b. Can occur in hyperparathyroidism
c. Paget’s disease may be a cause for it
d. All of the above
Ans to previous (March 2025)
B. two
MARCH 2025
Quote : The only way to do great work is to love what you do. Steve Jobs
HISTOPATHOLOGY
A 55 year old male patient presented with a mass in the
lumbar region, found to be at ultrasound in the renal/suprarenal position. Excision was done and the appearances are shown in fig 1 & 2 . Make you diagnosis. What could be the differentials?
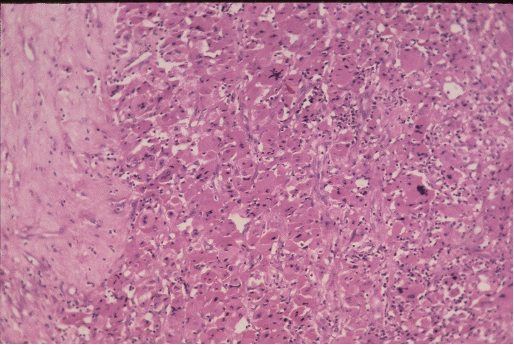
Fig 1
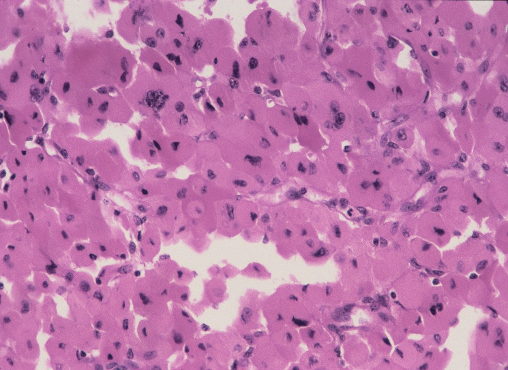
Fig 2
Ans to previous : (February 2025)
Tissue : Is endocervix
Lesion : Granulomatous inflammation consistent with tuberculosis.
CYTOPATHOLOGY
A 45 year old female patient presented with a swelling in the center of the neck, moved with deglutition. An ultrasound guided FNAC of the mass was done and showed the following appearances. What is your diagnosis?
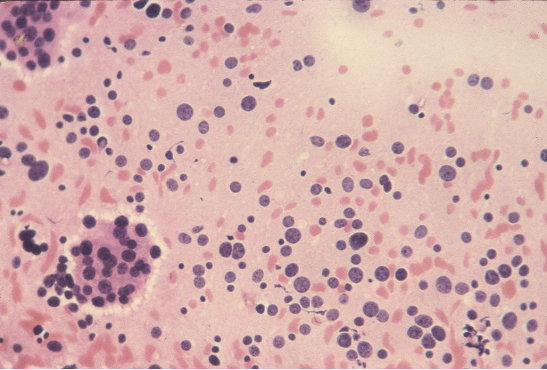
Ans to previous (February 2025):
• Leptotrichia or Leptothrix, are Gram-negative, non-spore-forming anaerobic organisms. They occur in the oral and vaginal cavities as very thin, segmented, large, filamentous structures
• the filaments are sheaths containing single rod-shaped cells that divide by binary fission, and do not branch.
TECHINQUES
Although genetic testing is available for many familial cancer syndromes, there are genes that have yet to be discovered. Each syndrome has special issues surrounding genetic testing;
In which of the familial cancers is genetic testing clinically recommended? Name some genetic cancers with known gene losses.
Ans to previous (February 2025):
Ans to previous
Automation is the independent accomplishment of a function by a device or system ( to carry out the function that was formerly done manually).
There are several machines used in the laboratory for various tests done in the lab.
Principle of tissue processing is that tissues are treated with various fluids using a series of solutions for a predetermined length of time in a controlled environment. Tissue thus processed is embedded in a medium such as paraffin which supports, it thus making it easy for sectioning.
2 principles are involved -
Tissue is housed in casettes placed in a perforated metal cylinder and moves through a series of chambers containing fluids arranged in the order desired. This cylinder is automatically transported through a series of reagents in the chambers (in the form of glass jars that are stationary); the basket of tissues travels from jar to jar.
Tissue is static and housed in a closed chamber and the series of fluid moves in and out of these chambers at pre-determined programmed regular intervals.
MCQ
How many nucleic acids does a human chromosome have ?
a. Three
b. Two
c. Four
d. One
Ans to previous (February 2025)
a. Simple / multinodular goitre
FEBRUARY 2025
Quote : Investment in Knowledge pays the best interest - Benjamin Franklin.
HISTOPATHOLOGY
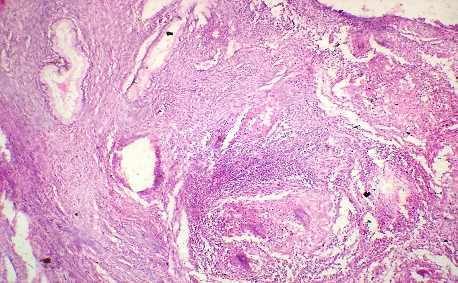
H&E x 100
Identify the tissue and the lesion.
Ans to previous : (January 2025)
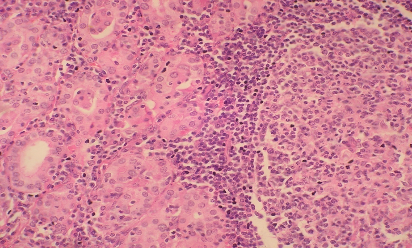
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Note : extensive nuclear change (clearing) should not lead to a mistaken diagnosis of papillary carcinoma. It can be rarely seen in nuclei in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Search also for pap fronds at FNA. Other areas on the same case with lymphocytic infiltration are shown in the fig below -
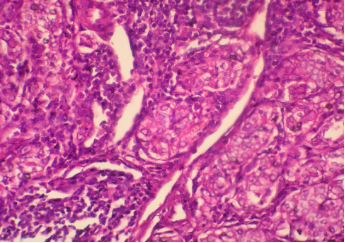
Note appearances of routinely seen histology of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (below) with no nuclear change for comparison with the above.
CYTOPATHOLOGY
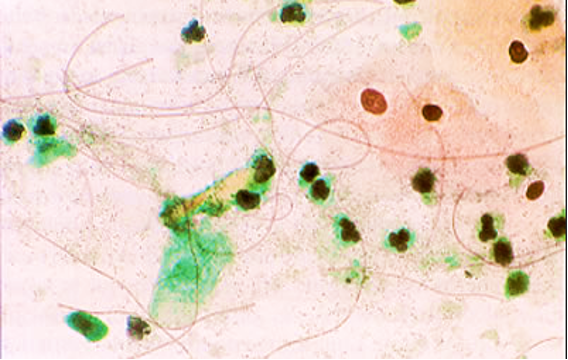
Identify the organism in the smear.
Ans to previous (January 2025):
Ans : Adenoma thyroid.
The close differentials at cytology are thyroid adenoma and follicular hyperplasia in a goiter.
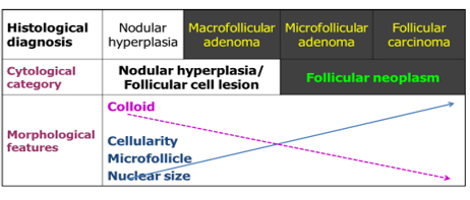
Two categories of follicular lesions are seen at FNA. 1. Follicular lesion (atypia) of undetermined significance - to be managed by repeat FNA 2. Follicular neoplasm (follicular or Hurthle cell neoplasm - to be managed most likely by surgical excision).
Diagrammatic rationale for cytologic diagnosis of follicular neoplasm.
TECHINQUES
Define automation in a pathology laboratory.
What are the principles involved in tissue processing?
Ans to previous (January 2025):
Use the Perl’s Prussion blue stain which stains iron blue in colour.
Principle : Haemosedirin contains ferric iron.
Ferric iron combines with potassium ferro cyanide to form ferric-ferro cyanide, which gives a bright blue colour (precipitate). This method demonstrates only ferric iron and not Ferrous iron.
Grading :
Gale’s grading system for iron in bone marrow. Click HERE
MCQ
Iodine deficiency usually gives rise to –
a. Simple/multinodular goitre
b. Solitary thyroid nodule
c. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
d. Diffuse thyroid gland enlargement
Ans to previous (January 2025)
A : surface antigen
JANUARY 2025
Quote : Life is 10% what happens to you and 90% how you react to it. Charles R Swindoll
HISTOPATHOLOGY
A 40 year old male with thyroid gland enlargement, more prominent on the right side. 2 figs are shown, make you diagnosis.
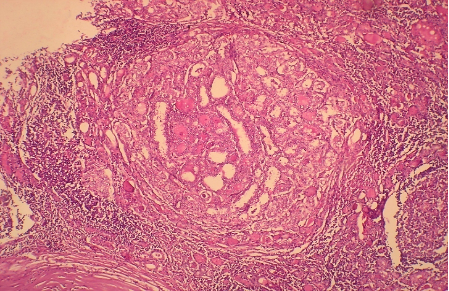
Fig 1 H and E x 100
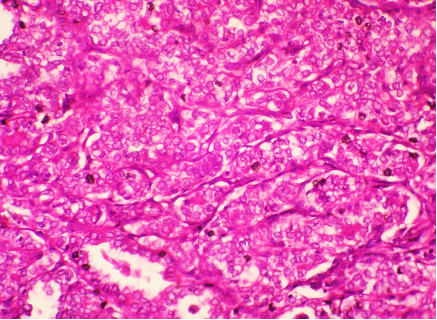
Fig 2 : H and E x 400
Ans to previous : (December 2024)
SEGA ie., Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma.
CYTOPATHOLOGY
Aspirate from a single nodule in the left lobe of thyroid gland, measuring 3.2 cms in size. Make you diagnosis .
What are the close differentials in a follicular lesion? How are they differentiated at cytology?
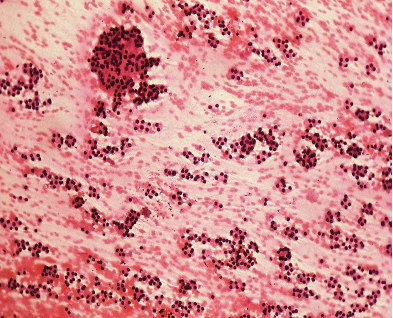
Ans to previous (December 2024):
• Inflammatory smear with parabasal and intermediate cells with atypical dense nuclei, with perinuclear halo.
• No typical koilocyte: ASC-US (LSIL?)
TECHINQUES
What stain would you use to detect the presence of iron in the bone marrow? What is its principle?
How is the grading on the presence of iron done?
Ans to previous (December 2024):
Formalin fixation
1. Place the specimen in a spacious container ( labelled with patient ID and specimen type) with fixative, ensuring that the specimen is fully submerged.
2. Section the specimen across if necessary to ensure better fixation.
3. Use a fixative-to-specimen ratio of at least 10 to 20 :1 to ensure thorough
penetration .
4. Fixation time : for small specimens 8-12 hours and for larger specimens 24 hours at least.
5. Preparation of 10% formalin : to 10 ml of commercial formalin (40%) add 90 ml of distilled water.
MCQ
In order to diagnose active infection of hepatitis B it is essential to demonstrate the presence of :
A. Hepatitis B surface antigen
B. Hepatitis B surface antibody
C. Hepatitis B core antigen
D. Increased ALT and AST
Ans to previous (December 2024)
D ie., all of the above
DECEMBER 2024
Quote : The bad news is that time flies. The good news is that you are the pilot! Michael Altshuler
HISTOPATHOLOGY
A 17 year old male patient presented with a mass lesion in the Foramen of Munro; and increased intracranial tension.
Radiological impression was “colloid cyst”.
Two images are given . Make your diagnosis.
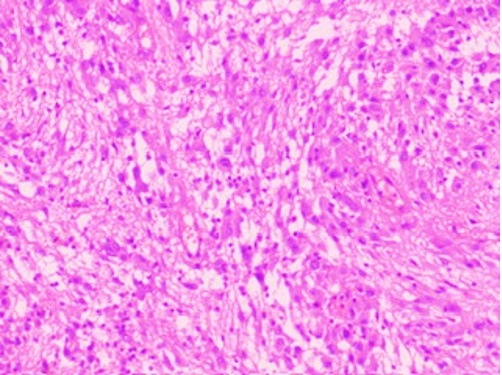
Fig 1 H and E x 100
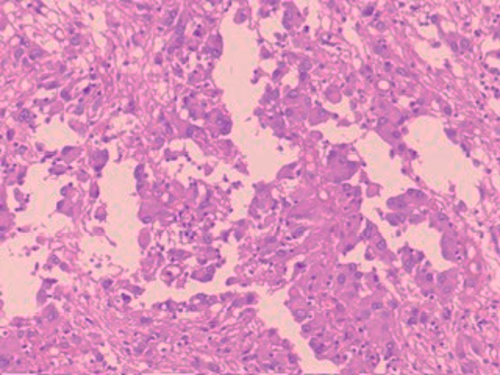
Fig 2 : H and E x 100
Ans to previous : (November 2024)
Adenocarcinoma lower lip, Glandular pattern +ve; Vacuolated cells with intracellular secretions .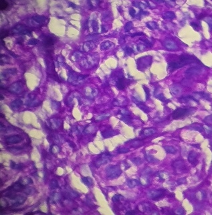
Fig above shows result of PAS stain with magenta stained intracellular secretions. The carcinoma probably arose from the minor salivary glands in the lower lip.
CYTOPATHOLOGY
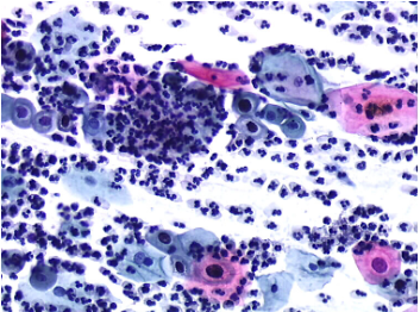
Pap stain x 20x
Guess the cell type; give your impression.
Ans to previous (November 2024):
Fungal filaments consistent with Mucormycosis. Hyphae are broad and non septate , no branching seen to suggest aspergillus filaments.

TECHINQUES
State the pre-requisites for formalin fixation.
Ans to previous (November 2024):
1. Microscopic examination of a drop of secretions.
2. KOH preparation: 20% KOH solution can be used on many types of samples, including skin scrapings, hair, cervical secretions & sputum.
3. Calcofluor white stain: this binds to fungal elements in a sample and fluoresces under UV light, making them visible the slide.
MCQ
Tuberous Sclerosis is –
A. is an uncommon genetic disorder that causes tumours to develop in many parts of the body
B. Associated with seizures
C. Mutations in either the TSC1 or the TSC2 gene.
D. All of the above
Ans to previous (November 2024)
Ans is : b
NOVEMBER 2024
Quote : We may encounter many defeats, but we must not be defeated. Maya Angelou
HISTOPATHOLOGY
A red ulcerated lesion on the lower lip of a 68 year old female. 2 figs , LP and HP are given below. Make your diagnosis. What histo chemical stain would you do to clinch the diagnosis?
From where is this carcinoma arising?
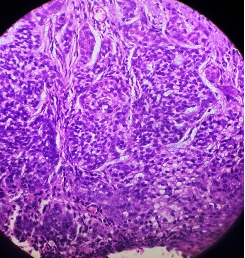
Fig 1 : (LP)
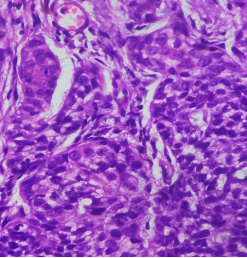
Fig 2 : (HP)
Ans to previous : (October 2024)
Renal Cell carcinoma -clear cell type.
The 2 factors at gross with a poor prognosis are the size of tumour ie 12 cms and the presence of necrosis. Presence of necrosis is considered an independent prognostic factor. The grade of tumour in the figs shown was given as 2 and stage was T2.
Grading of RCC :
A modified grading system for renal cell carcinoma (RCC) that incorporates tumor necrosis is as follows:
• Grade 1: ISUP grade 1 and non-necrotic ISUP grade 2
• Grade 2: Necrotic ISUP grade 2 and non-necrotic ISUP grade 3
• Grade 3: Necrotic ISUP grade 3 and non-necrotic nonsarcomatoid/rhabdoid ISUP grade 4
• Grade 4: Necrotic ISUP grade 4 and sarcomoatid/rhabdoid features
Tumor necrosis is an independent predictor of adverse outcome in RCC. This modified grading system outperforms the ISUP grading system and shows significant differences in survival between each grade.
Staging of RCC:
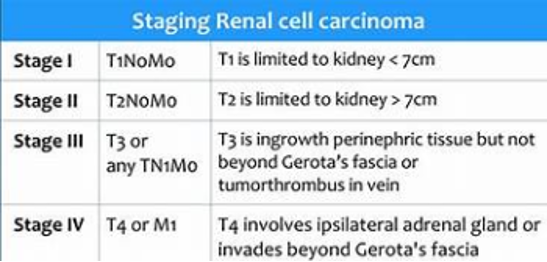
CYTOPATHOLOGY
A 52 year old male was clinically diagnosed with a space-occupying lesion in the left parietal lobe of brain. Squash and other smears were made .3 images are shown, make you diagnosis and why?
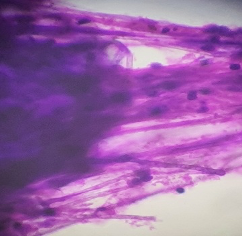
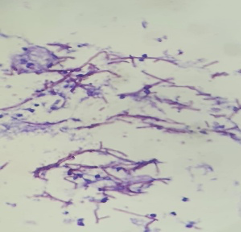
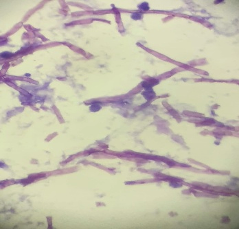
Ans to previous (October 2024):
It shows small cuboidal cells arranged in a tubular fashion . Cells appear bland, and resemble embryonic cell nests of kidney. A possibility of metanephric adenoma was given on the aspirate with a note to excise the same as a papillary carcinoma of the kidney cannot be excluded. Histology showed a benign metanephric adenoma. Patient was followed up for 5 years (then lost to follow up) and did well. Calcification is a feature of this tumour.
TECHINQUES
Name 2 methods of demonstrating fungi in secretions.
Ans to previous (October 2024):
a) Renal biopsies for staining of antibodies such as IgG, IgM, IGA, fibrin etc b) Detection of auromine labelled acid fast bacilli.c) Antinuclear antibodies detection in SLE and other autoimmune disorders; ANCA antibodies. d) Salt split immunofluorescence technique to differentiate pemphigus from epidermolysis bullosa acquisita e) In the detections of specific antigens, proteins, viruses, parasitic infections etc .f) Antinuclear antibodies detection in SLE and other autoimmune disorders; ANCA antibodies g) FISH to detect specific DNA segments h) Auto fluroscence in detection of formalin pigment and red fluorescence over green in neoplastic cancerous tissue.
MCQ
The minimum distance between the tissue and the walls of the Mold while embedding should be
a. 1mm
b. 2mm
c. 3mm
d. 4mm
Ans to previous (October 2024)
Ans is :
b) von Hippal Lindau disease
OCTOBER 2024
Quote : I can’ t change the direction of the wind but I can adjust my sails to always reach my destination. Jimmy Dean
HISTOPATHOLOGY
A 54 year old female presented with a renal mass of 3 years duration. Mass was excised. Make you diagnosis on the figs 1 to 4 provided showing the gross and microscopy.
What factors seen here grossly depict a poor prognosis? Give the grading and staging of RCC.
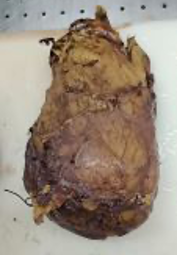
Fig 1 : Resected kidney with mass

Fig 2 : Cut section, mass measured 12 cms.
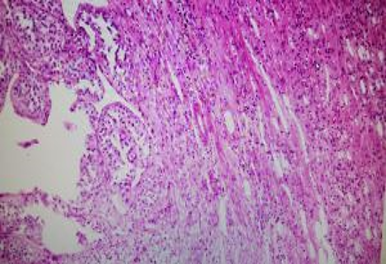
Fig 3 : low power view of neoplasm at histology. H&E x100
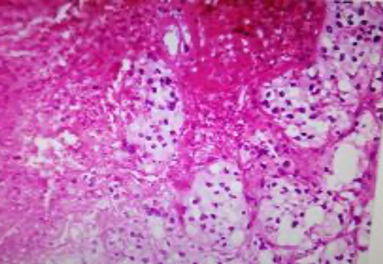
Fig 4 : High power . H& E x 400
Ans to previous : (September 2024)
Malignant melanoma. Perl’s stain to exclude haemosiderin and Schmorl’s stain, stains the pigment blue-green. Immunohistochemical markers for melanocytic differentiation, such as melan A, MART-1 (melanoma antigen recognized by T cell 1), HMB 45 (human melanoma black 45) (all three show cytoplasmic positivity), and S-100 (nuclear positivity) are often positive in melanocytic tumors.
The pigment is normally found in melanocytes in the skin, substantia nigra and eye.
CYTOPATHOLOGY
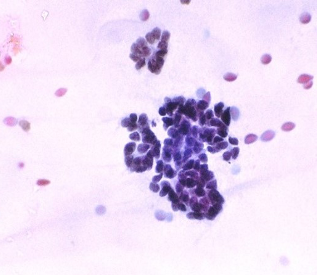
Ultrasound guided aspirate from a 2.5 cms mass in the upper pole of kidney in a 50 year male. Make you diagnosis or give the possibilities.
Ans to previous (September 2024):
Aspirate shows cells from malignant melanoma. The large intranuclear inclusion and clinical history of pigmented skin lesion lead to the possibility of melanoma at FNAC. Intranuclear inclusions may commonly be found in papillary carcinoma thyroid, RCC , etc. Confirmation is done by IHC marker on smear (melan A) or HMB 45 stain for the melanin pigment.
TECHINQUES
List the applications in diagnostic pathology where fluorescence is used as a prerequisite in the procedures.
Ans to previous (September 2024):
DOPA (deoxyphenylalanin) reaction is used in the diagnosis of amelanotic melanoma where pigment production is invisible grossly. It is a distinctive enzyme reaction and stains the invisible pigment of amelanotic melanoma, as the DOPA substrate is acted upon by DOPA-oxidase in the melanin-producing cells to produce a brownish black deposit. It differentiates undifferentiated carcinoma from amelanotic melanoma.
MCQ
The common hereditary disorder associated with RCC is
a) Down syndrome
b) Von Hippel-Lindau disease
c) Klinefelter’s syndrome
d) Williams syndrome
Ans to previous (September 2024)
Ans is :
d) – All of the above.
SEPTEMBER 2024
Quote : It is never too late to be what you might have been - George Eliot
HISTOPATHOLOGY
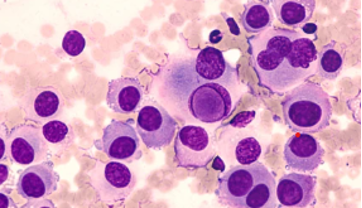
Make you diagnosis on the 3 figs given below (gross, low power & high power)
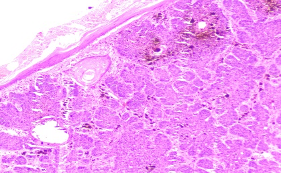
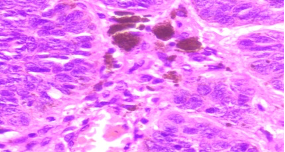
What special stains are done to clinch the origin of the pigment? Where is this pigment found in normal tissues?
Ans to previous : (August 2024)
The gross and microscopy (figs 1 to 4) show chronic non specific pyelo-nephritis with marked hydronephrosis. Note periglomerular fibrosis and dilated tubules.
CYTOPATHOLOGY
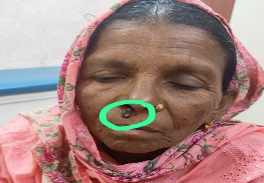
Aspirate from a pigmented nodule on the face. Make your diagnosis. What leads you to it? What would confirm it in the smear (not shown here)?
Ans to previous (August 2024):
TECHINQUES
What is DOPA reaction?
How does it help in diagnosis?
Ans to previous (August 2024):
Technique Ans : Fig 1 shows nuclear positivity in a dilated benign duct of a breast lesion (Maybe carcinoma in the vicinity. Breast tissue in section acts as internal control). It shows nuclear positivity.
Immunohistochemistry is increasingly used in the assessment of markers for breast cancer prognosis. If the result is positive for estrogen or progesterone receptors, it means that the patient is ER or PR+ and will respond to hormone therapy.
The most common method used in grading this positivity is the H-score which takes into consideration the staining intensity in conjunction with the percentage of cells staining positively in breast carcinoma.
A common scoring system is the Allred Scoring System. A similar approach to Allred score is demonstrated in so-called “quick score” system, with the differences in assigned values from 1 to 6 in proportion category A (of positivity) ; (1 = 0-4%, 2 = 5-19%, 3 = 20-39%, 4 = 40-59%, 5 = 60-79%, 6 = 80-100%) and 3 categories for intensity of staining; also multiplication is recommended instead of addition (as in the Allred score) for processing of the final score range. ( Detre S, Saclani Jotti G, Dowsett M. A “quick score” method for immunohistochemical semi-quantitation: validation for oestrogen receptor in breast carcinomas. J Clin Pathol. 1995;48:876–878. doi: 10.1136/jcp.48.9.876.)
Fig 2 : The marker used is Her2 new done routinely in breast carcinoma. Shows a 3+ positivity in the membrane of tumour cells. It is on the membrane surface that this receptor is located and positivity is read on the membrane.
IHC results for HER2 are reported as 0, 1+, 2+, or 3+. A score of 0, 1+, means the tumor is HER2-negative. A score of 2+ means the results are unclear and another test is needed, such as FISH. A score of 3+ means the tumor is HER2-positive.
One in five breast carcinomas show excess Her2 new expression.
MCQ
Melanin stains positively by –
A) Masson’s Fontana stain
b) Schmorl’s stain
c) Formaldehye – induced fluorescence
d) All of the above
Ans to previous (August 2024)
Ans is :
1. increased protein, increase in cells, specific gravity greater than 1.020
AUGUST 2024
Quote : The secret of getting ahead is getting started. Mark Twain
HISTOPATHOLOGY
Make you diagnosis on the figs 1-4 .
Fig 1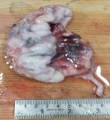 Fig 2
Fig 2 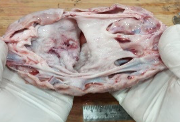
Fig 3 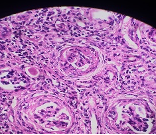
Fig 4 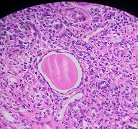
Ans to previous : (JULY 2024)
Tru cut biopsy shows features consistent with a benign phylloides tumour.
Fig 1 : Section shows fragments of stromal elements. The lower 2 fragments are cellular but no pleomorphism of the stromal cells is seen. Fig 2 shows a closer view with epithelial cells and stromal elements both of which are bland.
CYTOPATHOLOGY
Guided FNAC from a 1.9 cms nodule above the right kidney at MRI. Make your diagnosis.
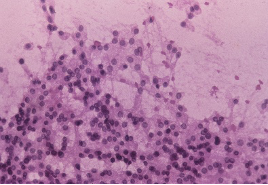
Ans to previous (JULY 2024):
Figs 1 and 2 : show FNAC appearances of the breast mass 5cms in size before a true cut biopsy was done. fig 1 shows a sheet of benign appearing ductal epithelial cells as well as stromal fragments and fig 2 a high power view of both elements; suggesting a bimodal patterned lesion favouring phylloides tumour.
TECHINQUES
Fig 1 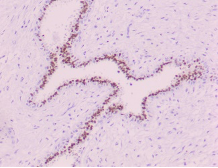
Fig 2 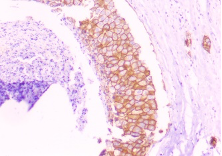
What could be the markers used in the IHC staining in Fig 1 and 2 Where is the positivity seen. How is this positivity graded and what does it mean?
Ans to previous (JULY 2024):
ACS recommendations for detection of early breast cancer in women with 'average risk':
- Women between 40 and 44 have the option to start screening with a mammogram every year.
- Women 45 to 54 should get mammograms every year.
- Women 55 and older can switch to a mammogram every other year, or they can choose to continue yearly mammograms. Screening should continue as long as a woman is in good health and is expected to live at least 10 more years.
(All women should understand what to expect when getting a mammogram for breast cancer screening )– what the test can and cannot do. Clinical breast exams are not recommended for breast cancer screening among average-risk women at any age.
ACS recommendations for detection of early breast cancer in women with 'high risk': Women who are at high risk for breast cancer based on certain factors should get a breast MRI and a mammogram every year, typically starting at age 30. This includes women who:
- Have a lifetime risk of breast cancer of about 20% to 25% or greater, according to risk assessment tools that are based mainly on family history (see below)
- Have a known BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutation (based on having had genetic testing)
- Have a first-degree relative (parent, brother, sister, or child) with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutation, and have not had genetic testing themselves
- Had radiation therapy to the chest before they were 30 years old
- Have Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Cowden syndrome, or Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome, or have first-degree relatives with one of these syndromes.
MCQ
Choose the best answer:
Oedema in acute inflammation is characterised by :
1. Increased protein, increased in cells, specific gravity greater than 1.020
2. Decreased vascular permeability
3. Decreased proteins, specific gravity less than 1012
4. Decrease in oncotic pressure.
Ans to previous (JULY 2024)
The diagnostic categories of the National Cancer Institute recommendations and their corresponding numerical codes in breast FNAC reporting are: Inadequate/insufficient (C1); Benign (C2); Atypical - probably benign /indeterminate (C3); Suspicious of malignancy (C4) and Malignant (C5). The answer here is iii.

